Bariatric Surgery: Types, Benefits, Comparison
Bariatric Surgery: Types, Benefits, and Why It May Be a Better Option Than Ozempic
In the global fight against obesity, two major approaches have gained attention: bariatric surgery and medications like Ozempic. While Ozempic (semaglutide) has surged in popularity due to its weight loss effects, bariatric surgery remains a more established, effective, and often long-term solution for individuals struggling with obesity and related health issues.
Table Of Content
What Is Bariatric Surgery?
Bariatric surgery refers to a group of weight-loss surgeries designed to help patients lose weight by limiting food intake, reducing nutrient absorption, or both. It is usually recommended for individuals with a BMI over 40, or over 35 with serious health conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea.
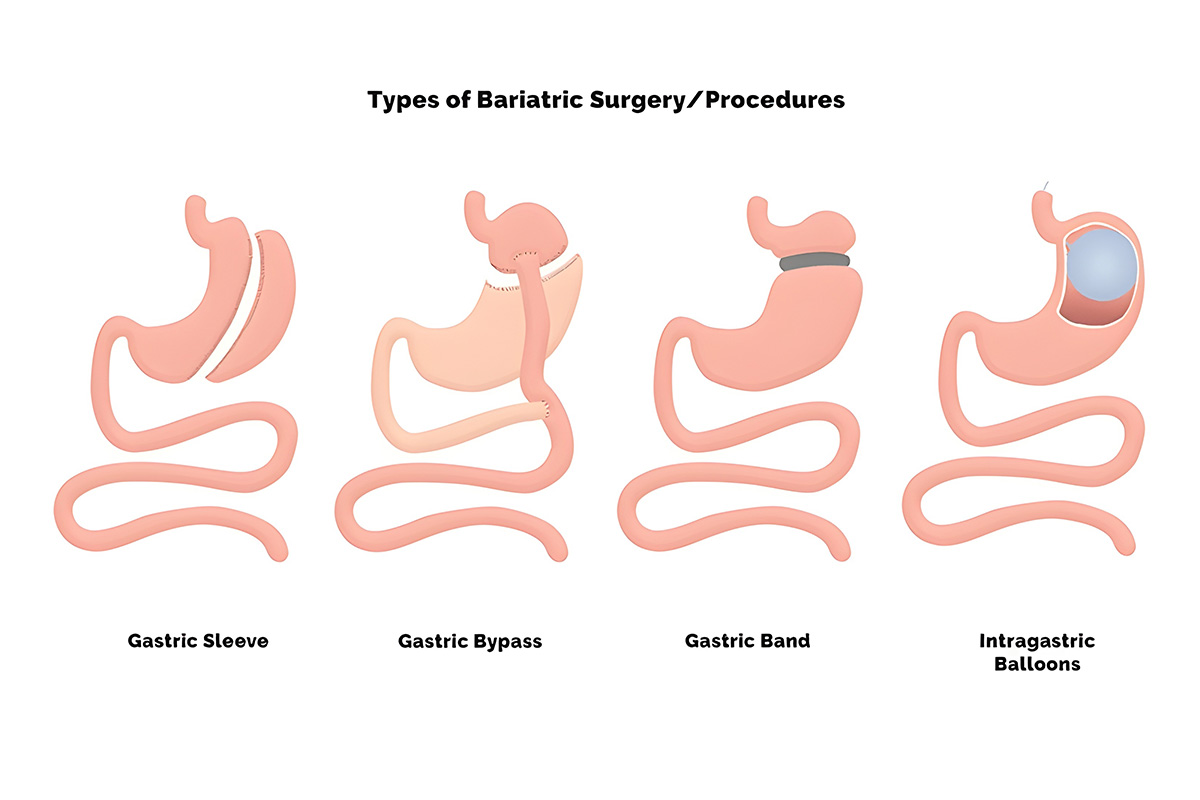
Common Types of Bariatric Surgery
- Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y)
This procedure creates a small stomach pouch and bypasses part of the small intestine, reducing calorie absorption and hunger hormones.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy
About 80% of the stomach is removed, limiting food intake and lowering ghrelin levels (the hunger hormone).
- Adjustable Gastric Band (Lap-Band)
An inflatable band is placed around the upper part of the stomach to create a small pouch, slowing digestion and promoting early satiety.
- Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS)
This complex surgery combines stomach reduction with a major bypass of the small intestine for both restriction and malabsorption.
Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
- Significant and Sustained Weight Loss
Many patients lose 60–80% of excess weight within 1–2 years.
- Long-Term Health Improvements
Bariatric surgery often resolves or improves conditions like type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and high cholesterol.
- Hormonal Balance
It leads to hormonal changes that reduce hunger and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Improved Quality of Life
Many patients experience increased energy, mobility, and mental health post-surgery.
Bariatric Surgery vs. Ozempic: Why Surgery May Be the Better Option
Both bariatric surgery and Ozempic can lead to weight loss, but they differ significantly in approach, results, and sustainability. Here’s how they compare:
| Feature | Bariatric Surgery | Ozempic (Semaglutide) |
|---|---|---|
| Weight Loss Results | 60–80% of excess weight lost | 10–15% of body weight lost |
| Long-Term Effect | Permanent (with lifestyle changes) | Temporary (weight often returns when stopped) |
| Cost | Covered by insurance (in many cases) | Expensive, often not covered long-term |
| Health Benefits | Can cure diabetes and hypertension | Improves glucose levels, limited long-term data |
| Hormonal Impact | Alters gut hormones significantly | Mimics GLP-1 only |
| Safety Profile | Surgical risks, but proven long-term | Mild to severe side effects (nausea, pancreatitis) |
Is Bariatric Surgery Right for You?
While medications like Ozempic can be helpful for short-term weight loss or for patients unable to undergo surgery, bariatric procedures remain the most effective long-term treatment for obesity. It’s important to consult with a bariatric specialist to understand which option aligns best with your health goals.
Conclusion
Bariatric surgery offers a transformative solution for individuals battling obesity. Unlike medications that require ongoing use, surgery provides lasting results and can reverse chronic conditions. For many, it’s not just about losing weight — it’s about reclaiming health and quality of life.